As the impact and consequences of the global climate crisis become ever more obvious, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword in the manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain industries, but rather a real and pressing concern. Companies are becoming increasingly aware of the need to reduce their environmental impact but also to improve process efficiency and working conditions in order to stay competitive and meet consumer demands. The transition to Industry 4.0, with its focus on automation, data exchange and analytics, is a step in the right direction. However, achieving true sustainability requires a holistic approach, and there is often friction between the goals of efficiency and sustainability. One technological approach that can help companies meet their sustainability goals is called “Real-time Locating Systems” (RTLS).
RTLS can leverage sustainability by accurately determining the location of assets and people, but the biggest challenge facing companies is the lack of harmonization among different real-time locating technologies and ecosystems for indoor and outdoor tracking, such as GPS, Ultra-wideband (UWB), Radio-frequency Identification (RFID) or Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). This article will highlight the benefits of RTLS related to sustainability, identify the biggest roadblocks for companies, and explain how to achieve RTLS harmonization with the right tools.
State of Sustainability in Manufacturing
Many manufacturing companies are transitioning into Industry 4.0, as it offers immense potential to reduce emissions and improve efficiency at the same time. This evolution is desperately needed since companies from industrial sectors are significant drivers of emissions. The logistics sector alone accounts for 23% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and without intervention, freight transport emissions are projected to more than double by 2050¹. In response, there has been a significant increase in investment in resource-saving technology in the industrial sector in Europe, already reaching $1.1 billion in 2022, surpassing 2021 levels significantly².
Studies by leading research institutes have also shown the potential for Industry 4.0 to significantly reduce energy consumption, carbon emissions, water consumption, waste, and raw material consumption. For example, according to a study by the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering, Industry 4.0 has the potential to reduce energy consumption by up to 30%³. A study by PwC estimates that Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, big data and analytics, and advanced robotics can reduce carbon emissions in manufacturing by up to 20%⁴. And according to the World Economic Forum, Industry 4.0 has the potential to reduce waste in manufacturing by up to 50%⁵.

The numbers speak a clear language. But how can these potentials be successfully leveraged? Many companies have already begun to incorporate the latest technological innovations, including Artificial Intelligence, 5G networks, as well as localization technologies such as Ultra-Wideband. With their help, material and production flows can be managed and monitored more effectively to gain a better understanding of workflows.
So-called “real-time locating systems” (RTLS) enable this transparency across the entire value chain.
What is RTLS and how can it help manufacturing companies become more sustainable?
Real-time locating systems (RTLS) refer to a set of technologies and methods used to accurately determine the location of an object in real-time. These systems can encompass a wide range of technologies and approaches, including sensor-based technologies such as GPS, BLE, UWB and RFID, and are designed to aid in the tracking, monitoring, and management of moving assets. Rather than being a specific technology or system, RTLS represents a broader goal of achieving real-time visibility and control over the location and movement of assets.
| Good to know: Different locating technologies, different use cases It’s important to note that not all locating technologies can be considered and used as an actual RTLS. In fact, RFID is primarily an Auto ID technology with the purpose of automatically identifying (not locating) things. Even though it has strong synergies with RTLS and is often mentioned in this context, these underlying differences typically mean a different use case focus. |
Does that sound new and innovative to you? Actually, it’s not. RTLS have been around for some time and, measured by the market volume for indoor positioning, are established worldwide. For example, an Allied Market Research⁶ estimates that the market volume for indoor positioning will reach 43.5 billion U.S. dollars by 2025. What is new, however, is the need to locate objects not only indoors, but both indoors and outdoors. And that’s why RTLS is becoming a repository of different, application-specific indoor and outdoor localization technologies. Each technology involved has its own specific strengths, weaknesses and use case focus, but in essence they can all be used to optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve safety.
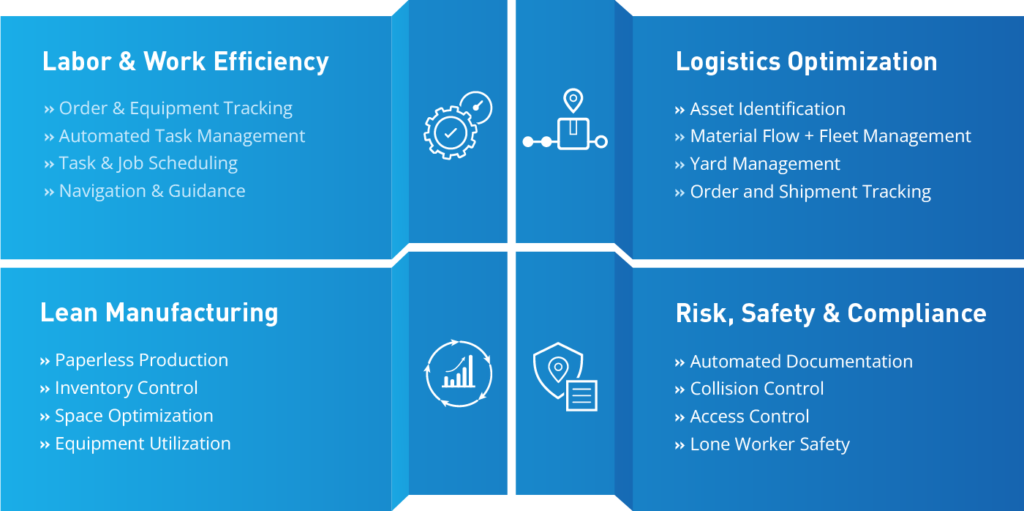
But it is not only from an operational perspective that the use of RTLS can make a big impact. RTLS is also an important factor in pursuing a broad spectrum of sustainability initiatives. Companies often have a history of multiple, independently operated RTL systems. These technologies are typically not interoperable and cause the RTLS infrastructure to operate inefficiently. By harmonizing proprietary technologies, the entire infrastructure of any given space ultimately becomes significantly more effective, as is the case with any technological framework. In the case of RTLS, this means that transportation routes can be optimized, warehouse and production space can be utilized more effectively, and employees can be deployed more productively, resulting in lower energy consumption and less emissions.
It’s without a doubt that RTLS can be an essential technology and enabler on the path to greater sustainability, but keep in mind: it is not the only one! There are multiple ways, methods and technologies that industries can adopt on their path to greater sustainability. For example, implementing energy-efficient equipment, using renewable energy sources, and implementing recycling programs. Additionally, companies can also adopt sustainable business practices, such as sustainable procurement, to reduce their environmental impact. Therefore it’s imperative to consider a holistic approach that takes into account multiple methods and technologies. That being said, RTLS represents a truly promising tool in this approach.
With that overview of RTLS out of the way, let’s dive deeper and explore how big of an impact it can make for the industrial sector.
3 major ways RTLS can drive sustainability in your company
From reducing emissions to improving working conditions, RTLS has the potential to drive sustainability in 3 major aspects:
Ecological Factors: Reorganizing transportation and operations
From an ecological perspective, RTLS can play a pivotal role in reducing emissions by improving the efficiency of transportation logistics. By optimizing routes and utilizing RTLS for real-time tracking and monitoring of vehicles and cargo, companies can greatly reduce transportation-related emissions and fuel consumption.
RTLS can have an impact on various environmental scenarios, but the following are the most critical:
- Enhancing supply chain visibility: RTLS close the white-spaces in existing supply chains by providing insights of parts, goods or equipment at suppliers. Is a good ready for shipment, has the truck already arrived at the yard? Answers to those questions provided by RTLS can result in a seamless end-to-end tracking, reducing friction and unnecessary transportation.
- Improving shopfloor and warehouse operations: RTLS can help companies track and monitor the usage of mobile equipment in warehouses, such as forklifts, AGVs, pallet trucks and workers, allowing for more efficient and optimized operations. This can lead to an immediate reduction in energy consumption and emissions.
Economical Factors: Efficient space utilization and asset optimization
From an economic standpoint, RTLS can represent a powerful tool for pushing sustainability to new levels. One of the key ways it can achieve this is by helping companies to make better use of their resources. For example, by using RTLS to effectively manage the utilization of warehouse space, companies can not only save costs associated with construction and maintenance, but they can also minimize their energy consumption and reduce the amount of space needed for storage. Furthermore, by using RTLS to optimize the way in which assets are utilized and managed, companies can cut down on the costs associated with acquiring new equipment, ultimately leading to a boost in their overall financial performance.
Other examples of economical improvements through RTLS are:
- Improved inventory management: RTLS can provide real-time visibility into the location and status of inventory, allowing companies to optimize their stock levels and reduce costs associated with overstocking or stock shortages.
- Automated processes and decision-making: RTLS can provide real-time data that can be used to automate processes and make data-driven decisions, which can improve efficiency and reduce costs. This includes areas like production, logistics and maintenance which represent costly operations for most companies. Automated processes also reduce or eliminate error rates, as manual or human interaction is no longer necessary.
- Improved maintenance management: RTLS can help companies track and monitor the usage and maintenance of their assets, allowing them to schedule and perform maintenance in a more efficient and cost-effective manner. This can lead to cost savings and increased longevity of assets.
For further insights, see our LIEBHERR solution example. This company was struggling to efficiently locate machine parts and components stored in their distribution centers. Using our RTLS harmonization middleware, the DeepHub, they were able to improve the utilization of 128,000 square meters of storage space and saved 200 hours in forklift usage per year.
Human Factors: Reduce unnecessary tasks and increase safety in the workplace
From a human perspective, RTLS can drive sustainability significantly by improving working conditions and reducing the risk of accidents. For example, minimizing travel and search times not only leads to more efficient personnel but also to more motivated employees. This is especially relevant for logistics companies with large scale warehouse operations and a reliance on a large workforce. Nothing is more frustrating for employees than unnecessary walks.
Other aspects of how RTLS is influencing employees are:
- A response to the shortage of skilled workers: RTLS automates processes that previously had to be done manually, such as scanning and booking operations. As a result, time-consuming and cost-intensive corrections due to errors are eliminated, employees can gain time to focus on their actual job or on further training. Overall, fewer resources are needed for the same work, allowing the existing workforce to be deployed where the shortage is greatest.
- Improved safety training: RTLS can provide real-time data on the location and status of assets and personnel, which can be used to develop and improve safety training programs for employees. This can help employees understand how to safely operate equipment and minimize the risk of accidents.
- Collision control: RTLS can be used to prevent collisions and accidents. By providing real-time alerts, RTLS can help companies to improve safety and working conditions for employees and avoid costly collisions and damage to equipment.

| Overwhelmed by the capabilities of RTLS? Learn more about how you can manage the transition to harmonized location technology in your organization in our blog article “What are the Top 5 Hurdles to Solutions in Logistics and Production?”. READ ARTICLE |
The need for a holistic RTLS approach is greater than ever before
The biggest challenge facing companies that want to address the above-mentioned potentials for increasing sustainability is the inconsistent technical infrastructure. Typically, a large number of different, proprietary RTLS are in use, which are not interoperable with each other. As a result, incompatibilities prevent many use cases from being covered, and the multitude of RTLS suddenly becomes an unpredictable cost driver. To tackle these issues and establish seamless real-time tracking, it is essential that these proprietary systems work together seamlessly. Only a holistic approach that interconnects all the technologies and systems can provide an effective solution. This is exactly where Flowcate comes in.
We are a global technology company that is committed to revolutionizing how location data is used in IoT by combining the unique power of locating technologies to provide a universal RTLS. We believe in the approach that no single technology is sufficient to build an effective and holistic RTLS, especially not one that covers both outdoor and indoor environments. Instead, combining different technologies is the key to success.
This belief was the foundation for us to play a vital role in the creation of omlox, the world’s first open locating standard which allows companies to implement flexible RTLS with components from any manufacturer in a fully interoperable manner. Omlox is now managed by Profibus and Profinet International and consists of a rapidly growing ecosystem of like minded and forward thinking companies with the goal to create the next generation of location-based service solutions. Learn more about omlox in this blog post.
The DeepHub is the premier omlox-compliant middleware which acts as the core of any omlox solution and the centerpiece for harmonizing RTLS. The software is open to all technologies and allows seamless tracking, creating transparency at scale. This is achieved by combining the strengths of different RTLS into one holistic RTLS that allows for truly streamlined and effective location-data management.
Through its extensive partner ecosystem, including solution providers, system integrators, hardware providers, RnD and technology partners, we are paving the way for omlox-based solutions on a broad spectrum. Our vendor-independent middleware enables partners to integrate and combine every locating technology, allowing for the creation of new digital business models and a competitive advantage by harnessing the full potential of location data.
Together we can make a true impact by enabling partners from a multitude of specialties to build solutions that enable the reduction of resources and optimization of processes on a path to sustainability.

A peek into the future: Harmonized RTLS data will lead to entirely new possibilities
Let’s think big: It is not only an efficiency push – and the positive sustainability aspects – that are possible with RTLS harmonization. Instead, standardized location data opens up entirely new possibilities for reorganizing business models or processes. At the same time, a consistent and comprehensible set of data across the entire value chain is also important for fulfilling increasingly rigorous reporting requirements and creates competitive advantages for companies.
One opportunity is to enter the circular economy, which allows manufacturers to trace their products throughout the entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. By understanding the lifecycle of their products, companies can identify areas for improvement and increase the overall sustainability of their operations.
Another important consideration for companies is the increasing requirement for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) data to be disclosed in financial reports. For processes under their control, such as Scope 1 and 2 emissions, this is relatively straightforward. However, for activities that occur within the supply chain or logistics (Scope 3 emissions), data is often lacking or not standardized. By implementing and harmonizing RTLS, companies can gain a better understanding of their entire value chain, including emissions from suppliers and logistics, and use this information to improve their reporting and overall sustainability.
Finally, some companies may choose to use their sustainability efforts as a competitive advantage. For example, if a company can prove that they produced less CO2 than they were allowed to according to their CO2 certificates, they can sell the unused certificates on the market. This can be a powerful incentive for companies to not only meet, but exceed their sustainability goals. With the help of RTLS, companies can gain a detailed understanding of their operations, identify opportunities for improvement and ultimately, demonstrate their commitment to sustainability to customers and investors.
Whether it is constant improvements in the framework of interoperability or the development of completely new business models that only become possible through the harmonization of RTLS: seamless asset tracking in real-time has a measurable impact on economic and ecological factors of any company. If the world continues to slide at top speed into the global climate crisis, these refinements in the entire value chain can make a crucial contribution to securing the existence of corporations and SMEs for decades to come.
This is why our day-one mantra at Flowcate is: We connect the dots to make the world a little bit better – day by day.
References
¹ Global Logistics Emissions Council Framework for Logistics Emissions Accounting and Reporting, Version 2.0
² Industrial Tech Report, 2022 Update
³ https://www.ipk.fraunhofer.de/en/media/futur/futur-2020-1/l4ee.html
⁴ https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/industrial-products/next-manufacturing.html
⁵ https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/04/how-ai-can-cut-waste-in-manufacturing/
⁶ https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/indoor-location-market
